LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) Battery Introduction
What is Lithium Iron Phosphate?

Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4 – CAS number 15365-14-7) also known as lithium ferro phosphate (LFP), for use as the cathode material for lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). LiFePO4 has high specific energy (90 – 170 Wh Kg-1), high volumetric energy density (1200 kJ L-1) and offer good cyclic performance ((typically 2000-5000 cycles) with nominal cell voltage (~3.2 Vs. Li/Li+).
Lithium iron phosphate has a wide but flat exothermic reaction peak at 250 – 360 °C with a much smaller heat release of 147 J g-1. The strong P–O covalent bond prohibits oxygen release thus promoting intrinsic safety which is the top priority of an electrical vehicles (EVs). Also with relatively Low cost, long battery life, no cobalt content, it makes LFP battery cells desirable for mass production for in EVs.
Technical Data
| CAS Number | 15365-14-7 |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | LiFePO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 157.76 g/mol |
| Chemical Name | Lithium Iron Phosphate |
| Synonyms | Lithium Ferro Phosphate, LFP, LFPO |
| Classification / Family | 2D semiconducting materials, Battery materials, Metal oxides, Cathode materials |
| Colour | Black powder |
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Powder

| Resistance | 115 Ω cm |
|---|---|
| Tap Density | 1.13 g/cm3 |
| SSA | 12.2 m2/g |
| Particle Size | ~1.5 µm (D50) |
| pH | ≤8.9 |
| Discharge Efficiency (First) | 97.5% |
| Capacity (First) | 155.5 mAh/g |
Crystal Structure

The triphylite lithium iron phsophate (LiFePO4) belongs to the olivine family of lithium ortho-phosphates. LiFePO4 has an orthorhombic crystal lattice structure in the space group Pnma. The unit cell structure is represented by corner-shared FeO6 octahedra and edge-shared LiO6 octahedra running parallel to the b-axis, linked together by the PO4 tetrahedra.

When lithium iron phosphate is coated with 2 wt% of the electrochemically exfoliated graphene layers, it is able to reach 208 mAh g-1 in specific capacity. Binder-free SWCNT modified LFPO cathode delivers a superior rate capacity of 161.5 mAh g-1 at 0.5 C and 130.2 mAh g-1 at 5 C, with a high-rate capacity retention of 87.4% after 200 cycles at 2 C.
What is a Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery?

The lithium iron phosphate battery (LiFePO. 4 battery) or LFP battery (lithium ferrophosphate) is a type of lithium-ion battery using lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO. 4. ) as the cathode material, and a graphitic carbon electrode with a metallic backing as the anode.
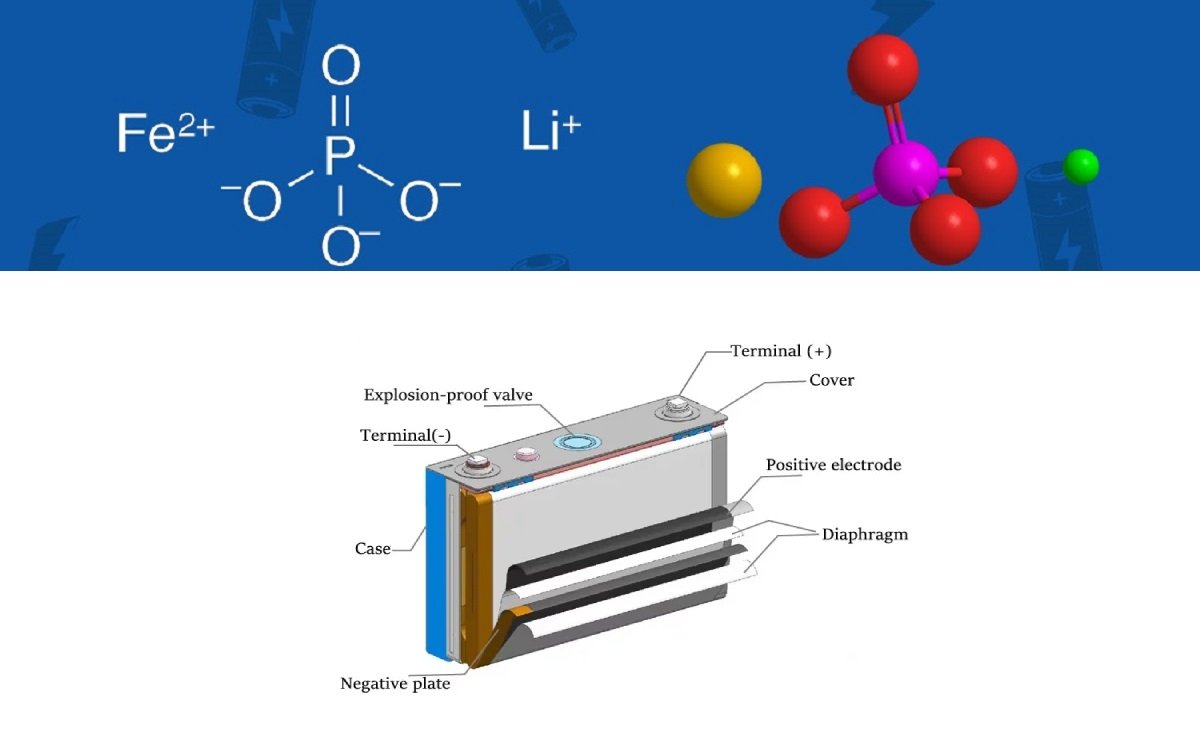
Structure Of Lithium Cells
As below picture, the structure of cells are main made up of Cathode, Anode, And electrolyte and separator.

Working Principle Of LiFePO4 Battery
The LiFePO4 battery is an olivine structure of LiFePO4 as the positive electrode of the battery, which is connected to the positive electrode of the battery by an aluminum foil. The center is a polymer diaphragm, which separates the positive electrode from the negative electrode. However, Li+ can move freely but the electron e- can not move. The negative electrode of the battery is on the right, which consists of carbon (graphite) and is connected to the negative electrode of the battery by a copper foil. The battery’s electrolyte is hermetically enclosed by a metal shell and located between the upper and lower ends.
A separator creates a barrier between the cathode and anode, preventing the electrodes from touching while allowing electrical charge to flow freely between them.
The cathode is metal oxide, and the anode consists of porous carbon. During discharge, the ions flow from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte and separator. Charge reverses the direction and the ions flow from the cathode to the anode.
Below picture illustrates the process

As the successor to the conventional lead-sulfuric acid battery chemistry, modern lithium-ion batteries have become established not only in portable electrical devices and in electromobility. Although these are more expensive to buy than classic lead-gel batteries, particularly high energy densities can be achieved with lithium-ion technology with space and weight savings of up to 75%. Lithium is the lightest metal in the periodic table and at the same time has ideal electrochemical properties for the realization of high specific energy densities (Wh/kg). The number of charging cycles, the achievable depth of discharge DoD (Depth of Discharge) and the service life are also many times greater than with lead-gel batteries.
With each full cycle (charge/discharge), the lithium-ion cell is subjected to chemical, thermal and mechanical stresses (expansion), which cause cell aging. In particular, charging with high currents (rapid charging) and at low temperatures can lead to lithium plating on the anode. Here, the lithium ions are not stored in the graphite layer structure of the anode as intended, but are metallically deposited on the surface of the graphite anode and thus lead to significant performance losses or even short circuits within the cell. High end-of-charge voltages or even overcharging also lead to strong heat generation, expansion and stress on the lithium-ion cell.
LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery known for their specific advantages and wide range of applications. Here’s a detailed look at their benefits and uses:

Advantages of LiFePO4 Battery:
- Safety:
- Thermal Stability: LiFePO4 batteries are more thermally and chemically stable than other lithium-ion batteries, reducing the risk of overheating and thermal runaway.
- Non-Toxic: The materials used in LiFePO4 batteries are non-toxic and environmentally friendly.
- Long Cycle Life:
- Durability: These batteries can endure more charge-discharge cycles (typically 2000-5000 cycles) compared to other lithium-ion batteries, making them long-lasting.
- Slow Capacity Fade: They exhibit slower capacity degradation over time.
- High Discharge Rate:
- High Power Output: LiFePO4 batteries can deliver high discharge currents, making them suitable for high-power applications.
- Wide Temperature Range:
- Operational Flexibility: They perform well across a broad temperature range, from -20°C to 60°C, which is beneficial for various environmental conditions.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate:
- Long Shelf Life: The self-discharge rate is lower than many other battery types, meaning they retain their charge for longer periods when not in use.
- Eco-Friendly:
- Recyclable: LiFePO4 batteries are more environmentally friendly due to the absence of heavy metals and their recyclability.
Applications of LiFePO4 Battery:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs):
- Cars, Buses, and Bikes: Due to their high power output and safety, LiFePO4 batteries are widely used in electric vehicles.
- Scooters and Golf Carts: Their durability and long cycle life make them ideal for smaller electric vehicles.
- Renewable Energy Storage:
- Solar Power Systems: LiFePO4 batteries are commonly used in solar energy storage systems due to their long life and reliability.
- Wind Energy Storage: They are also used in wind energy systems for efficient energy storage and release.
- Portable Electronics:
- Power Tools: High discharge rates and durability make them suitable for power tools.
- Medical Devices: Their safety and reliability are crucial for medical equipment.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS):
- Backup Power: LiFePO4 batteries are used in UPS systems for critical backup power in data centers, hospitals, and other essential services.
- Marine and RV Applications:
- Boats and Yachts: Their ability to perform in a wide temperature range and high safety standards make them ideal for marine use.
- Recreational Vehicles (RVs): Long cycle life and reliability are beneficial for RVs.
- Grid Storage:
- Large-Scale Energy Storage: LiFePO4 batteries are increasingly used in grid storage solutions to balance supply and demand, and to store energy from renewable sources.
Conclusion:
LiFePO4 batteries offer a compelling combination of safety, longevity, and performance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications from consumer electronics to large-scale energy storage systems. Their eco-friendly nature and ability to operate under various environmental conditions further enhance their appeal in today’s energy-conscious world.


